Context
One of the most pressing problems of a globalized economy is moving money, however the “money” or “currency” may have been defined. Moving it across the world, at a fair cost, with appropriate transparency and in real time.
The world is not there yet, and the problem still represents a great opportunity to build a business around it. Business-to-business segment of the global payments industry presents a rather unique opportunity.
Imagine a fintech startup, with access to seed money of about $3 million based in the Middle East, attempting to capitalize on the business-to-business payments in the emerging markets in the region.
Their key assets include a strong set of relationships with financial institutions and regulators across MEA along with founders who are experienced in the B2B payments business.
This document attempts to explore a possible approach to building such a startup by describing a baseline strategy. This of course is theory, and much iteration is required for execution over a substantial amount of time, but this idea has to start somewhere, and this is the start.
Observations; Facts, Opportunities and Risks
Facts
Global payments industry has grown tremendously over the last decade and has witnessed an inflow of large investments. Along with the focus from governments on building and improving domestic and cross border payments infrastructure, the payments industry is set to continue this growth. The global B2B market was estimated to be worth around 125 trillion U.S. dollars in 2023 and would be close to $150 trillion in the next few years.
According to a report by McKinsey, global payments revenue would reach $3 trillion annually by 2026 with B2B payments representing a larger share relative to that of B2C(retail) payments. The Asian market is expected to be the strongest region in terms of revenue share, followed by North America, EMEA and LATAM.

Some of the larger players, with valuation exceeding a billion dollars and some closing in on $50 billion are mentioned below.

These are global and regional players with the key underlying proposition being a global payments network, and use cases on top of the network to cater to segments such as PSPs, financial institutions, platforms, marketplaces, money transfer operators, mobile money operators, merchants, and digital banks.
The table below lists a few key uses cases which are offered in the B2B payments industry. The fundamental aspect of most of these organizations is a strong global payments settlement network, some focus more on a certain geography like Asia or LATAM, and others on certain segment of payments, like payments for small and medium businesses and others prioritize large corporations.
Commoditized capabilities are making payments such as international fund transfer, payrolls, mass payouts and collections are offered via simple API integrations.
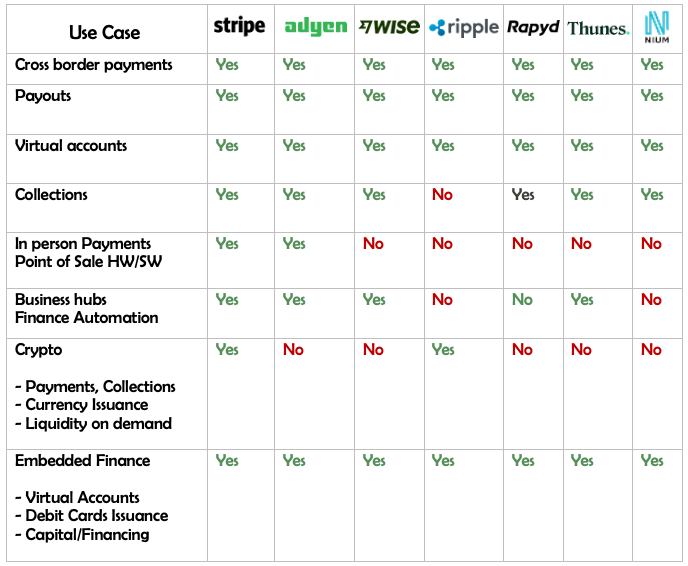
Other niche use cases are to offer payments and collections in crypto currencies, some organizations like Ripple also offer private currencies and an ecosystem associated with it offering liquidity on demand to businesses.
Offering virtual accounts that can be funded is one of the most essential capabilities that B2B payments organization offers.
Embedded finance (or a subset of banking as a service, which is a more popular term) is becoming essential part of the business, with key capabilities being virtual accounts, card issuing, capital and financing. This segment is expected to grow, with large ticket items like insurance, wealth management being most obvious inclusion.
Operational capabilities are also a popular part of the business but is usually offered to relatively larger corporations with the key feature being a “business hub” that offers capabilities to manage all payments, collections, cards issuing and acquiring, across all countries of operation.

Opportunities
- The size of the market is growing at close to ~9% annually, even though retail payments segment has seen much more investments and focus, B2B payments despite all the competition, still represents a great opportunity.
- As the global payments infrastructure develops further, it would have a major impact in this segment.
- Despite increasing competition, not all countries, regions across the globe are similar in terms maturity, this represents an opportunity to build business locally and then take it global.
- Business-to-business (B2B) payments represents a large untapped market.
- A fintech that with focus on building a settlement network reaching every part of the world, leveraging financial institutions, other regional networks, PSPs, could represent a great potential to build a business around. Starting with a focus on a uncatered regional markets in developing world and expanding slowly across the world.
- Cost differentiation with tech and relationships (governments etc. for licenses) and focus on complex use cases for a high value target segment, this approach could provide a potentially strong moat.
Risks
- High entry barriers and relatively longer period required to go to market. B2B Payments is a mission critical, highly regulated industry.
- Funds required to build a feasible business model would require substantial capital over a long period.
- Growing competition globally, even though easier to build a network of network but difficult to gain cost differentiation and eventually profitability.
- This would be an operations intensive business, that would require substantial resources over a long time period with high-risk impact of failure for high value transactions.

Proposed Strategy
The Hypothesis
A global business can be built by leveraging the growth in B2B payments industry which is estimated to processes US $125 trillion worth of transactions annually, by building a global payments network of networks offering global reach at a major cost differentiation to PSPs, domestic and regional digital banks and large corporations in developing countries across the world.
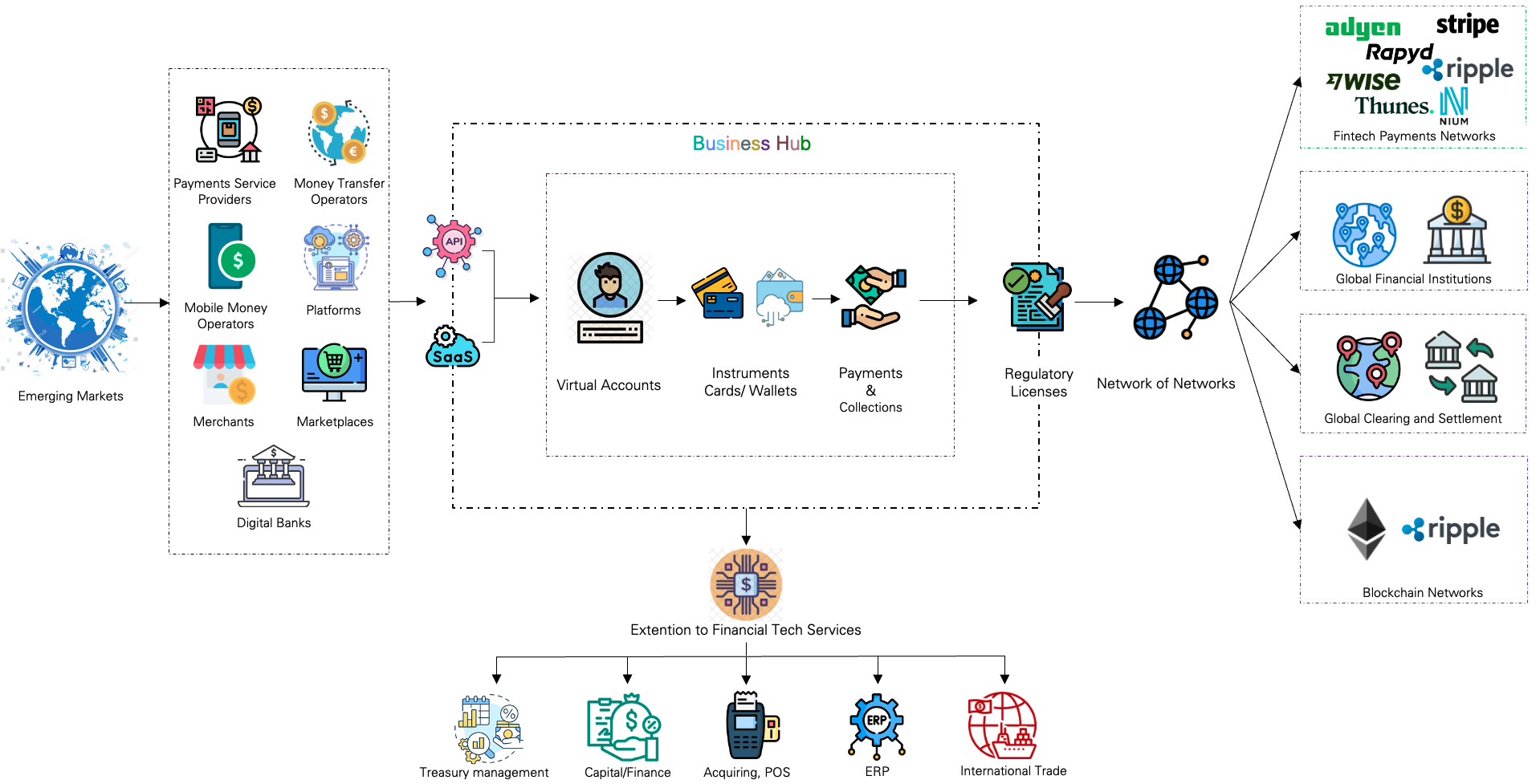
The following sections describes three key steps to reach a point of traction for the startup.
Step one, build the underlying core payments “network of networks”.
Build a global payments network of networks, by leveraging financial institutions, layer 2 and layer 3 payment networks run by fintechs. The network should be capable of both fiat and digital currencies settlement, supporting all sorts of transactions for a varied type of businesses. All this while acquiring appropriate regulatory licenses in countries of interest would be essential, though this is easier said than done.
Financial institutions
The general perception is that banks are losing the payments volumes and as a virtue of that they are giving away payments business to fintechs. This is partially true, a major chunk of the payments revenue, majorly on the payments channel and initiation side has moved to the fintechs, but the clearing and settlement still remains with financial institutions that are connected to central payments infrastructure via the central bank or regulators under the supervision of central banks (referred to as layer 0 in the document).
A relationship with key financial institutions and banks (referred to as layer 1 network) in the countries of interest is absolutely essential for payment settlement. Offering a business model lucrative to the banks is essential for a sustainable long-term collaboration.
Layer 2 & 3 global payments networks
Besides the financial institutions and banks, multiple layers of payments interconnected network operate in different geographies and customer segments. Collaborating with them to leverage their reach at a fair cost and transparency would give the business a quick market access. These networks would then get access to payments volume that the business generates.
Ripple is a good example of layer 2 network, and Thunes, Wise are good examples of a layer 3 payments network, who also plug into layer 2 and layer 1 network.
Payments networks offering settlement of digital currencies
Access to the payments networks capable of comprehending digital currencies across the spectrum; regulated digital currencies like central bank digital currencies, regulated stablecoins, and unregulated currencies like bitcoin, Ethereum and other private currencies is an essential distinction for current customer base and growth in the near future.
The growth in tokenized assets is pushing settlement with digital currencies on a blockchain based network, and businesses in this segment are set to increase as regulators build guidelines around them across the world.
Acquiring appropriate regulatory licenses
On top of building the payment network, acquiring appropriate regulatory licenses in the countries of interest would be critical to offer services on this network. A few common types of payments licenses across the world are mentioned below.
Most of the countries uses a version one of these licenses, the terms used to describe them may differ but the capabilities that they provide are similar in nature, depending on the regulatory status of the country.
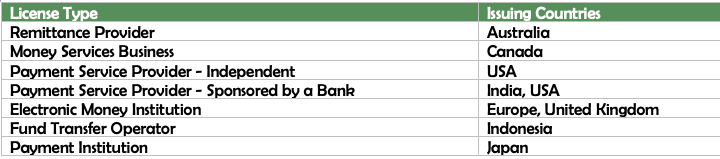
In the long term, the business would be wise to not shy away from acquiring a banking license to get control of a deeper set of facets across the value chain.
Step two, prioritize use cases with relatively higher level of complication.
The objective is to cater to segment with lower levels of competition, and higher barrier to entry. Building a strong network would enable the fintech to build and enhance relationships with key players in the banking infrastructure, regulators, central banks, financial institutions etc.
Leveraging these relationships would then aid in executing “Step two” of the proposed strategy.


Step three, start with countries in emerging markets.
Start with a country in underrepresented in regions such as North Africa, East Africa, LATAM, offering to PSPs, Digital Banks and MTOs. As this gets tractions, scale to similar other uncatered markets across the world.
- Domestic and regional Payment service providers
- Domestic digital and neo banks.
- Money transfer operators and exchange houses.
 From this point on, in next stages the fintech should focus on identifying similar markets and replicating the approach and offer the services via accelerated API integrations and SaaS business hubs to businesses.
From this point on, in next stages the fintech should focus on identifying similar markets and replicating the approach and offer the services via accelerated API integrations and SaaS business hubs to businesses.
Defining the MOAT
![]()
- Global reach to “Easy – Hard – Rare” markets across the globe.
- Cost differentiation – Delay break-even to gain customer base in early stages.
- Relationships – Regulatory licenses and relationships with regulators and financial institutions, payments networks for settlement.
- Accelerated GTM with technology – offering services with APIs and/or SaaS Business hubs.
Strategy execution approach
It would be critical to have a high-level view of the following fundamental questions while building a corporate and business strategy to execute the approach described above,
- What products and services would be sold? Defining basic products, services, and value proposition.
2. Who would the products and services be sold to? Defining initial customer segments.
3. How would the product and services be sold? Defining tactical execution along with standards and processes.

What products and services would be sold?
Defining basic products, services, and value proposition.
A global payments and collection network for settlement of traditional assets and tokenized assets. Leveraging the network, various capabilities listed below across “payments” and “collections” would be part of the services. Three essential aspects of the offering would be an ability own a virtual account, instruments in form of cards and digital wallets to use the funds in the virtual account along with payments and collections capabilities.

The intent would be to tap into partnerships with fintech players to offer an extended set of services such as financing, POS network, international trade services.
Who would the products and services be sold to?
Defining initial customer segments.
The focus should be of countries in emerging markets, with limited options across domestic and international payments. Regional financial services players would be targeted, the list below describes the key target segment.

- Payment service providers, with a regional and domestic scope usually do not have the reach across the globe, and even if they do, it’s not on the most appropriate terms from a commercial perspective.
- Money transfer operators are essential parts of the global remittance business, more so in the emerging markets.
These businesses are becoming digital and there are large whitespaces in payments that can be catered to.
- Platforms and marketplaces are one of the biggest business model innovations of recent times, and the variations are increasing by the quarter.
Segments such as, creator economy and sharing economy are key reasons for this high growth market offer a lot of potential.
- Digital merchants are growing and need cost effective solutions to do their business across the globe.
- Banks, specifically domestic and regional digital banks need to reach markets to cater to their customers payments, this is not always a fair deal, and presents good opportunities for a B2B payments business.
How would the product and services be sold?
Defining tactical execution along with standards and processes.
The business would focus on offering global reach with a major cost differentiation, driven by APIs led propositions and a subscription, transaction-based business hubs for businesses across emerging economies.

Conclusion
Business to business payments industry is a canvas which is still relatively uncluttered. The problem is global in nature, and it is connected with almost every aspect of the world economy. If the approach described in this document is taken as a baseline strategy, there is a great potential to build a business positively impacting businesses and people around the world.

